Fallen Arches Causes And Symptoms
Overview

Flat feet can develop as an adult ("adult acquired flatfoot") due to injury, illness, unusual or prolonged stress to the foot, faulty biomechanics,[5] or as part of the normal aging process. Flat feet can also occur in pregnant women as a result of temporary changes, due to increased elastin (elasticity) during pregnancy. However, if developed by adulthood, flat feet generally remain flat permanently.
Causes
Factors that increase your chance of flat feet include family history, diseases that cause muscle or nerve damage, such as peripheral neuropathy, diabetes, cerebral palsy, spina bifida, or muscular dystrophy. Foot injuries. Conditions of the feet that can injure foot tissue such as osteoarthritis. Conditions present at birth, such as excess laxity of joint capsules and ligaments, such as Ehlers-Danlos syndrome. Obesity.
Symptoms
Pain and stiffness of the medial arch or anywhere along the mid-portion of the foot. Associated discomfort within and near the ankle joint. The knees, hips, and lower back may be the primary source of discomfort. Feet may often feel tired and achy. Painful shin splints may develop with activity. Gait may be awkward.
Diagnosis
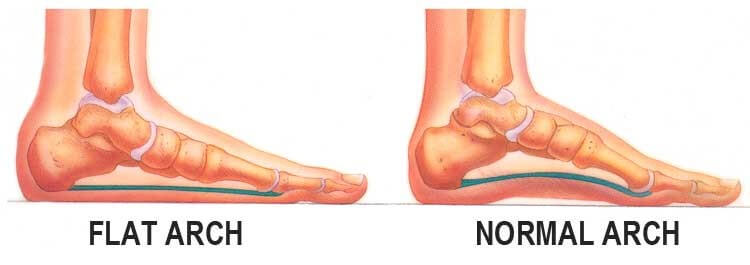
You can test yourself to see if you have flat feet or fallen arches by using a simple home experiment. First, dip your feet in water. Then step on a hard flat surface, like a dry floor or a piece of paper on the floor, where your footprints will show. Step away and examine your foot prints. If you see complete/full imprints of your feet on the floor, you may have fallen arches. However, it?s important to seek a second option from a podiatrist if you suspect you have fallen arches so they can properly diagnose and treat you.
What causes pes planus?
Non Surgical Treatment
Have you found yourself in the store looking at all the different foot care products? There is everything from massaging gel insoles to foam arch supports and heel cushions. If your arches fall the same amount on each side, you might be able to use an insert off the shelf. If they fall differently, then a generic insert will not fix the imbalance. If you have a high arch, a generic insert will likely not be high enough for full correction. Good custom orthotics provide a number of advantages over the generic inserts that you find in the store. Custom orthotics can take into account your body weight and degree of flexibility in your foot, not someone else?s. They also account for the anatomical differences in your feet. The corrected height of one arch is often higher in one foot than the other. A G-Laser foot analysis can provide you with this information.
Surgical Treatment
Generally one of the following procedures is used to surgically repair a flat foot or fallen arch. Arthrodesis. One or more of your bones in the foot or ankle are fused together. Osteotomy. Correcting alignment by cutting and reshaping a bone. Excision. Removing a bone or a bone spur. Synovectomy. Cleaning the sheath that covers the tendon. Tendon transfer. Using a piece of one tendon to lengthen or replace another. Arthroereisis. placing a small device in the subtalar joint to limit motion. For most people, treatment is successful, regardless of the cause, although the cause does does play a major role in determining your prognosis. Some causes do not need treatment, while others require a surgical fix.

Flat feet can develop as an adult ("adult acquired flatfoot") due to injury, illness, unusual or prolonged stress to the foot, faulty biomechanics,[5] or as part of the normal aging process. Flat feet can also occur in pregnant women as a result of temporary changes, due to increased elastin (elasticity) during pregnancy. However, if developed by adulthood, flat feet generally remain flat permanently.
Causes
Factors that increase your chance of flat feet include family history, diseases that cause muscle or nerve damage, such as peripheral neuropathy, diabetes, cerebral palsy, spina bifida, or muscular dystrophy. Foot injuries. Conditions of the feet that can injure foot tissue such as osteoarthritis. Conditions present at birth, such as excess laxity of joint capsules and ligaments, such as Ehlers-Danlos syndrome. Obesity.
Symptoms
Pain and stiffness of the medial arch or anywhere along the mid-portion of the foot. Associated discomfort within and near the ankle joint. The knees, hips, and lower back may be the primary source of discomfort. Feet may often feel tired and achy. Painful shin splints may develop with activity. Gait may be awkward.
Diagnosis
You can test yourself to see if you have flat feet or fallen arches by using a simple home experiment. First, dip your feet in water. Then step on a hard flat surface, like a dry floor or a piece of paper on the floor, where your footprints will show. Step away and examine your foot prints. If you see complete/full imprints of your feet on the floor, you may have fallen arches. However, it?s important to seek a second option from a podiatrist if you suspect you have fallen arches so they can properly diagnose and treat you.
What causes pes planus?
Non Surgical Treatment
Have you found yourself in the store looking at all the different foot care products? There is everything from massaging gel insoles to foam arch supports and heel cushions. If your arches fall the same amount on each side, you might be able to use an insert off the shelf. If they fall differently, then a generic insert will not fix the imbalance. If you have a high arch, a generic insert will likely not be high enough for full correction. Good custom orthotics provide a number of advantages over the generic inserts that you find in the store. Custom orthotics can take into account your body weight and degree of flexibility in your foot, not someone else?s. They also account for the anatomical differences in your feet. The corrected height of one arch is often higher in one foot than the other. A G-Laser foot analysis can provide you with this information.
Surgical Treatment

Generally one of the following procedures is used to surgically repair a flat foot or fallen arch. Arthrodesis. One or more of your bones in the foot or ankle are fused together. Osteotomy. Correcting alignment by cutting and reshaping a bone. Excision. Removing a bone or a bone spur. Synovectomy. Cleaning the sheath that covers the tendon. Tendon transfer. Using a piece of one tendon to lengthen or replace another. Arthroereisis. placing a small device in the subtalar joint to limit motion. For most people, treatment is successful, regardless of the cause, although the cause does does play a major role in determining your prognosis. Some causes do not need treatment, while others require a surgical fix.